ODM vs Contract Manufacturing

- What Is Original Design Manufacturing?
- What is Contract Manufacturing?
- ODM vs CM: A Direct Comparison
- ODM vs CM: Selecting the Right Model
Table of Contents
Introduction
Original design manufacturing (ODM) is a manufacturing model in which a customer orders quantities of an existing product from the manufacturer, essentially ordering “off-the-shelf” products. On the other hand, in Contract Manufacturing (CM), a business designs and develops a new or unique product and contracts a manufacturer to produce it from scratch. In both models, the customer brands, markets, and sells the products as their own.
ODM and CM are the opposite ends of the 3rd party contract manufacturing spectrum in terms of IP ownership, design control, ease of purchasing, supplier speed to market and other characteristics. The processes involved, level of investment, and customer involvement are disparate, making it imperative to understand the difference between the two models and which is the appropriate choice for your project.
This article explores ODM vs CM, how these outsourced manufacturing models work, their applications, distinct advantages and disadvantages, and how these factors affect a business. The article also comparatively analyzes ODM vs CM to assist businesses in making well-informed choices on the appropriate model for their needs, goals, and resources.
What Is Original Design Manufacturing? Understanding ODM
ODM is an outsourced manufacturing model in which a customer (business) contracts the manufacturer of an existing product to produce and brand the product on the customer's behalf. The business then markets and sells the products as its own. This model is a common type of private label manufacturing.
In this model, the manufacturer/supplier, known as the original design manufacturer, handles the entire product development process. They have ready-made designs, tooling, material suppliers, and an established supply chain for the product(s) they manufacture. They are also responsible for any tests, certifications, and quality assurance processes the product may require. In addition, the manufacturer owns the intellectual property (IP) rights to the product's design and tooling.
Typically, in ODM, the products are either ready-made or have a set design that the customer can minimally alter, with modifications that don't impact the manufacturer's product's tooling, as this is also used for other customers. The modifications a customer can request usually include custom branding like color changes, logo addition, custom packaging, etc., and slight design variations such as button style, handle placement, and the addition of accessories.
Various levels of businesses, from solopreneurs to large corporations, utilize ODM. A significant number of ODM customers are small-scale private label businesses focusing on the marketing and sales aspects of the business. Many sellers on retail chains such as Amazon and independent platforms like Shopify are private label businesses that order existing products from manufacturers and brand, market, and sell them as their own.
What is an example of ODM manufacturing model?
Large corporations and well-known brands that sell products comprising several parts also commonly use ODM to source the parts. A good example is the relationship between PC manufacturers and Intel - a manufacturer of processors. Intel manufactures and sells standalone processors that end users can buy. However, they mainly serve as ODM processor manufacturers to PC brands like HP, Asus, and Lenovo. The PC brands order the "plug-and-play" processors from Intel without any modifications and integrate them into their PCs. Intel retains all IP rights to the processors and can sell to both HP and Lenovo, fierce competitors in the PC industry. If the PC brands could request specific processor designs and specifications, that would be another one of the different types of outsourced manufacturing models.
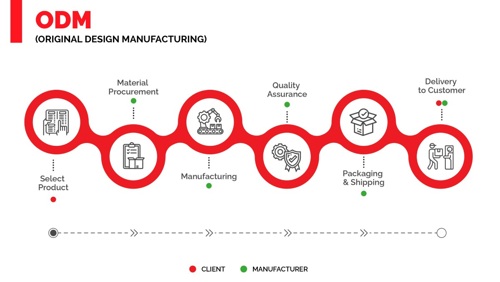
Fig. 1: ODM Manufacturing Process
Advantages of ODM
Some of the advantages of original design manufacturing for businesses are as follows:
- The customer is free of the bulk of responsibilities in the product development process, as the manufacturer handles this. The customer simply has to order the products.
- The business saves significant time and resources on designing and testing new products, as the products already exist on the market.
- Original design manufacturers have vast experience in designing and manufacturing a particular product. They also have access to reliable suppliers and supply chains. These factors often translate to higher product quality.
- The product development timeline is significantly reduced as the manufacturer already has ready-made designs and tooling. The manufacturer may even have inventory available for immediate delivery.
Disadvantages of ODM
Original design manufacturing also has the following inherent limitations:
- Because the manufacturer designs the product and tooling, they, and not the customer, own full IP rights to the product.
- ODM doesn't allow for extensive customization. The customer can only request slight design changes that don't require modifications to the manufacturer's existing tooling.
- In most cases, the customer has minimal control over the manufacturing process.
- ODM customers often end up with the exact products as their competitors, as manufacturers produce the same products for multiple customers.
What is Contract Manufacturing? Understanding CM
Contract manufacturing is an outsourced manufacturing model in which a business designs a product and then contracts a manufacturer to produce it. The product may be an end-use product or a component part of a bigger system.
In this model, the customer (business) designs and develops a unique, functional product and hands the design to the manufacturer to create the product. Generally, contract manufacturers do not specialize in specific products or have ready-made designs, tooling, or products. Instead, they have dedicated facilities for producing unique tooling for different designs. The manufacturer takes the customer's design, makes the required custom tooling, and manufactures the product. Being responsible for the initial product design and development, the customer holds the IP rights to the product and its tooling.
Contract manufacturing offers businesses high control and flexibility in the product development cycle. This model also exists in various forms that differ in execution and is often regarded as an umbrella model for several other models. In contract manufacturing, a client may contract a supplier at the design, testing & prototyping, manufacturing, or assembly stage of the product development timeline, having handled the preceding stages. When a business contracts a single manufacturer to handle everything from design to delivery, this constitutes turnkey manufacturing. Additionally, if a client contracts a manufacturer to assemble ready-made parts into finished products, this is known as contract assembly.
What is an example of the CM manufacturing model?
Contract Manufacturing (CM) is a business model where a company hires another company to produce specific components or products on their behalf to their drawing and specification. The design and the design validation is handled by the customer, while the contract manufacturer is acting as a service provider, selling their manufacturing know-how and facilities. A classic example of this is Apple's relationship with Foxconn. While Apple designs its iconic iPhones in California, and is deeply involved in determining components specifications, designating component suppliers, testing the product intensely, etc. it has hired Foxconn, a Taiwanese contract manufacturer, to actually make the millions of units of the iPhone in its factories in China. Apple provides the design and specifications, and Foxconn handles the mass production planning, assembly, and quality control of the product. This partnership allows Apple to focus on design, innovation, marketing, and sales, while Foxconn, with its manufacturing expertise, handles the complexities of large-scale production.

Fig. 2: Contract Manufacturing Process
Advantages of contract manufacturing
Contract manufacturing offers the following benefits:
- Contract manufacturing offers businesses more control of the product development timeline, as they are typically handling the design, testing and other aspects of the development process.
- Customers are responsible for the product design and can develop unique and new products with distinct builds, materials, and functionalities.
- The customer holds the IP rights to the product design and tooling.
- A customer doesn't have to entirely rely on one supplier for the different aspects of product development. Identifying and replacing an erring contractor handling a particular aspect is easier.
Disadvantages of contract manufacturing
The following are some of the disadvantages of CM:
- Customers have to handle a significant amount of responsibilities, including design, prototyping, and material procurement. These responsibilities increase the complexity of product development and require substantial effort and resources from the business.
- Creating and validating new designs, sourcing materials, building new tooling, and establishing supply chains (required for unique products) all increase product time to market in CM projects.
- Dealing with multiple contractors for different aspects of production increases the possibility of mishaps, such as supply chain delays.
ODM vs CM: A Direct Comparison
ODM and CM have various critical differences. Understanding these differences and how they can impact a business is crucial.

Fig. 3: Turnkey Manufacturing at Komaspec
Customer involvement and control
This is one of the most crucial differences between ODM vs CM. In ODM, customers are hardly involved in product development and have no control over it. They simply order the products, and the manufacturer handles everything from design to delivery of the finished products. Depending on the agreement, the customer may request proof of relevant qualifications and certifications for the product. On the upside, this absence of control directly relieves the business of any manufacturing responsibilities.
Conversely, in contract manufacturing, the customer bears a significant portion of the responsibilities. However, this means they have much greater control. The customer provides the product designs and stipulates materials. They can also request specific tests and QA processes. In addition, the customer may be aware of the manufacturer's capabilities, processes, suppliers, and supply chain.
Product uniqueness
Another vital difference between ODM vs CM is product uniqueness. In CM, the customer designs their products from scratch, enabling them to create truly unique or new products and build a brand identity. On the other hand, ODM only offers customers the "what you see is what you get" option. The exact product already exists. The customer can only request minimal modifications.
IP rights
IP rights for ODM products belong to the manufacturer, as they are the party handling the product design, validation and testing. The minor design alterations the customer may make are insignificant in IP rights considerations. A manufacturer may offer a customer some form of product exclusivity at a specified minimum order quantity.
Contract manufacturing, on the other hand, typically allows the customer to control all IP if they have the appropriate agreements in place with the manufacturer.
Product development timeline (Time to market/delivery)
Original design manufacturing offers a much faster product development timeline than CM. ODM manufacturers have readymade designs, tooling, and products, thus eliminating product development's design, testing, and tooling stages. Any slight modifications a customer requests will not significantly impact the timeline. This speed allows businesses to order and receive their goods in a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the order quantity and the customization.
Conversely, in CM, substantial time is spent on designing, prototyping, testing/certifying, and tooling a new or unique product from scratch, significantly increasing production timelines to 6 to 18 months and above.
Cost
As is the case with time, the availability of ready-made designs and tooling significantly reduces the initial investment costs for ODM customers, as the manufacturer bears these costs. The manufacturer also benefits from economics of scale when ordering from their suppliers. While the manufacturer may amortize these costs into the product, the cost per unit will be low, especially for large order quantities. Price is directly proportional to order quantity.
Businesses using the contract manufacturing model spend substantial resources designing, developing, testing, and tooling their product. These costs translate to higher costs per unit.
| MODEL | ODM | CM |
| Product Ideation | Client | Client |
| Research & Development | Factory | Client |
| Product Testing | Factory | Client |
| Product Manufacturing | Factory | Factory |
| White or Private-Label Offerings | Factory | Client |
| Branding | Client | Client |
Table 1: OEM vs CM Manufacturing
ODM vs CM: Selecting the Right Model for Your Business
After comparing ODM vs CM, the next step is selecting the suitable model for your business. The following are factors to consider to enable you to choose a model that matches your business' specific goals, needs, and resources.
- Control over design and manufacturing: CM gives customers significant influence over design, materials, tests, and QA processes. This control is especially vital for companies that sell critical or complex products, as they are liable for any mishap or defaults the products have as the owner of record. More complex and critical products often require the level of control that CM offers. This is why pure, build to print style contract manufacturing is often used for medical devices, food and pharmaceuticals, etc.
- Product differentiation: ODM products are off-the-shelf, so they are by definition, not unique or highly differentiated. Contract manufacturing allows customers to create truly unique products, with special features, new designs, functions, etc.
- IP rights: In contract manufacturing, businesses retain all rights to their designs, toolings, and products, making custom manufacturing the better option for IP-sensitive or new, innovative products.
- Time to market: When time-to-market is the most critical consideration in selecting an approach, ODM is the appropriate choice, as this will allow customers to get product ready fast..
- Cost: Cost per unit of ODM products are typically less than their CM counterparts.
- Production volume: Significant initial investment costs go into designing and developing a unique product in contract manufacturing. This makes it economically impractical to produce very small quantities of the product with this method, or for the manufacturer to carry too much stock.
In contrast, ODM manufacturing can be used for both large and small order quantities for a product, as the design and tooling already exist, and the customer may be able to even combine production with others or buy from excess stock.
Business resources
Both large corporations like HP and micro-retail businesses utilize ODM for various reasons. However, small businesses without the resources to design, test, and order large quantities of unique products are better off using the ODM model.
| Criteria | ODM | Contract manufacturing |
| Design & Manufacturing Control | No customer involvement | High levels of customer involvement and control |
| Product Differentiation | Minimal | Highly |
| Design and tooling IP rights | Belong to manufacturer | Belong to the customer |
| Initial Investment costs | Low - ready-made designs and tooling | High - product design, certification and tooling |
| Product development timeline | 1-2 Months or less | From 6-18 months, depending on product complexity and design validation |
Table 2: ODM vs CM: Selecting the right model
Conclusion
ODM offers a fast, inexpensive way to get generic products with minimal investment and hassle. On the other hand, custom manufacturing enables businesses to get unique, proprietary products while providing full control over the production process, but requires a corresponding higher investment of time and resources. Which model makes sense for any given company is going to be highly dependent on the target market, the resources available and their capabilities.
About Komaspec
Komaspec is an industry-leading outsourced manufacturing solutions provider with a reputation for quality and reliability, providing manufacturing services for customers worldwide across a wide range of sectors. We offer complex mechanical and electromechanical product assembly, sheet metal processing in our dedicated plant, injection molding, welding, CNC machining, stamping, and other services. We have a full-service team of engineers and professionals to push projects quickly and efficiently.
Contact us, and an expert member of our team will promptly reach out to you on how best we can collaborate on your next project. Partner with us today to harness the immense benefits of turnkey manufacturing for your next project.
Works Cited
- “What is OEM vs ODM, Komaspec” https://www.komaspec.com/about-us/blog/oem-vs-odm-manufacturing/
- “What is private label” Shopify, https://www.shopify.com/blog/what-is-private-label
- “Intel” Tech Target, https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/Intel
- "ODM, OEM, CM – Which type of manufacturer should you pick for your project?" Komaspec, https://www.komaspec.com/about-us/blog/odm-oem-cm-which-type-of-manufacturer-should-you-pick-for-your-project
- “What is turnkey manufacturing” Komaspec, https://www.komaspec.com/about-us/blog/what-is-turnkey-manufacturing/
- “What is Contract Assembly?” Komaspec, www.komaspec.com/about-us/blog/what-is-contract-assembly/
